What is digital security?
Digital security aims to ensure that the digital environment is reliable, safe and accessible. This requires that different actors are able to prepare for threats to the digital environment, withstand disruptions and recover from them as well and as quickly as possible. Securing everyday functions also requires extensive cooperation, shared operating models and willingness to develop them.
Digital security implementation areas also extend beyond the digital world. In other words, digital security is not a separate entity from the rest of the organisation or society, but an integral part of all their activities. In the same way, it is also part of everyone's everyday life and manifests itself as uninterrupted communication, services and other activities in the digital world.
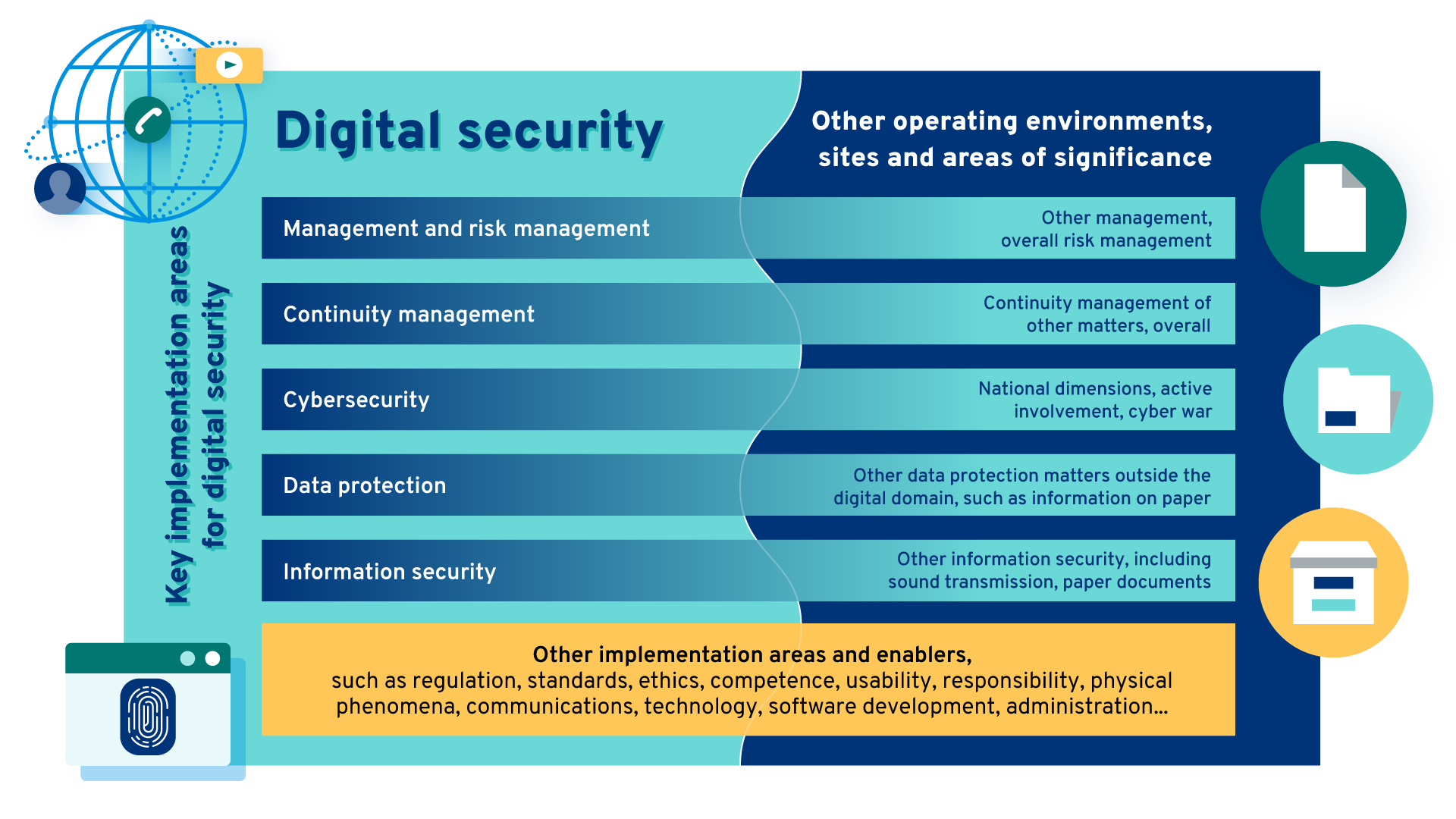
Digital security implementation areas
Digital security can be defined from many different starting points. Five key implementation areas are necessary to ensure comprehensive digital security. These include management and risk management, continuity management, cybersecurity, data protection and information security.
The organisation of digital security requires management and risk management. Digital security management should therefore be a natural part of the management, administration and overall security of the entire organisation.
Risk management includes the risk assessment process and the planning, implementation, monitoring and correction of measures. Risk management is an essential part of proactive management and organisation's decision-making.
- An example from the perspective of an organisation: The organisation's operating methods are developed based on identified threats and opportunities.
- An example from the perspective of an individual: Everyone can observe and identify the risks associated with using digital services and strive to manage them by acting carefully.
Continuity management means preventing disruptions, preparing for them, recovering from them and managing their impacts, and ensuring the continuity of the organisation's operations.
- An example from the perspective of an organisation: The organisation safeguards its own operations or, for example, societal security of supply by preparing for disruptions.
- An example from the perspective of an individual: Everyone can prepare for temporary cut off of their electricity or water supply by reserving sufficient daily supplies for their home.
Cybersecurity refers to the security of an electronic and networked society or organisation. It aims to safeguard vital and critical functions of society or the organisation.
- An example from the perspective of an organisation: Water supply and energy supply systems must be protected with particular care against disturbances and faults.
- An example from the perspective of an individual: Everyone can protect themselves from influencing information by being critical of content online.
Data protection means protecting people's privacy and protecting personal data from unlawful use in all situations.
- An example from the perspective of an organisation: Patient data must be handled carefully to prevent it from being accessed by outsiders.
- An example from the perspective of an individual: Everyone can take care of their personal data by carefully considering which digital services they enter them into.
Information security refers to measures aimed at ensuring the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information. The aim of information security is to ensure that only the relevant parties have access to the information they need.
- An example from the perspective of an organisation: The organisation shall ensure that tasks are performed only on the organisation's equipment and the digital services approved by it.
- An example from the perspective of an individual: Everyone can secure their own data by keeping their passwords carefully and making them sufficiently long and complex.
What does a digital environment mean?
Our society has rapidly digitalised. Almost all of our information and messages move through digital networks and platforms. Data is collected from each of us for the electronic services of public administration and companies. A digital environment refers to all information systems in which information is processed in different ways using software, devices or networks.
Examples of digital environments include instant messaging services, banking and payment services, e-learning environments, social media platforms and production management systems. In addition to electronic devices and systems, the digital environment includes people using them and their activities.
Additional information
This definition of digital security is based on the OECD definition (pdf in Finnish) and the Government Resolution (pdf). More detailed definitions for different terms and digital security management can be found in the VAHTI risk management vocabulary (pdf in Finnish).
